
Over the past few years I’ve made a living managing Internet of Things (IoT) software development projects. In that time I’ve come to learn a number of protocols for communicating sensor and telemetry information back to “the cloud”. Among the most popular in the IoT space is MQTT, a lightweight protocol that allows for publishing messages to topics, as well as the ability to subscribe to topics. This model is frequently refer to as “pub-sub“.
In addition to working with IoT and MQTT, I am passionate about Swift and the inroads it is making into the server space since being open-sourced and ported to Linux. Naturally it made sense to combine the two areas and start working on an MQTT client implementation in Swift! We’ve taken the liberty to port an iOS implementation of an MQTT client over to Swift 3.0 on a Linux platform. In general this is an example that, indeed, Swift will be making inroads into both the server and IoT domains.
A disclaimer before we get started: the code below is based upon Swift 3.0 which is going through developer previews on Linux right now. To get started with Swift 3.0 on your Ubuntu 14.04 or 15.10 system go here. Or, if you have an armv7 device such as BeagleBone Black, try the ARM port of Swift 3.0!
Sample Application
My first idea was to put together a cool BeagleBone MQTT client that was reading one of the ADC inputs and sending it up to the broker. The input was going to be from a Microchip MCP9700 temperature sensor IC. The sensor IC maximum output voltage is 5.5V so I knew a voltage divider would be involved to keep the voltage input to the BeagleBone under 1.8V. I had the voltage divider all sketched out and everything!
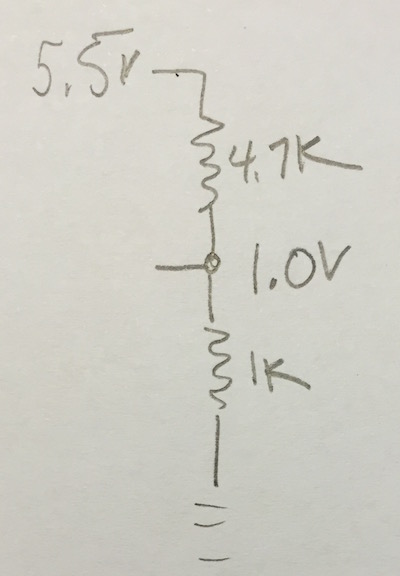
Unfortunately while testing the sensor IC with a standard match I got the flame a little too close to the IC package and well, Project Icarus came to an end. Our replacement example is a bit less ambitious, but serves the role of learning how to build an MQTT client with Swift. And it doesn’t involve matches.
MQTT
Our application is built around a port of a client MQTT library (yay open source!). We’ve named it simply MQTT and posted it to GitHub. The library is meant to be used in a Swift application that you can create as follows:
|
1 2 3 |
mkdir PubSysTemp cd PubSysTemp swift package init --type executable |
Running swift package init --type executable is going to give you a Swift project shell (think npm init) that you can begin customizing for your purposes. We’re going to edit Package.swift and add our MQTT library dependency:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import PackageDescription let package = Package( name: "PubSysTemp", dependencies:[ .Package(url:"https://github.com/iachievedit/MQTT", majorVersion:0, minor:1) ] ) |
MQTT Client Delegate
The design of the MQTT library is such that you will create a client class that inherits from MQTT and MQTTDelegate. A very basic implementation looks like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
import Foundation import MQTT class Client:MQTT, MQTTDelegate { init(clientId:String) { super.init(clientId:clientId) super.delegate = self } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didConnect host: String, port: Int) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didConnectAck ack: MQTTConnAck) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didPublishMessage message: MQTTMessage, id: UInt16) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didPublishAck id: UInt16) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didReceiveMessage message: MQTTMessage, id: UInt16 ) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didSubscribeTopic topic: String) { } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didUnsubscribeTopic topic: String) { } func mqttDidPing(mqtt: MQTT) { } func mqttDidReceivePong(mqtt: MQTT) { } func mqttDidDisconnect(mqtt: MQTT, withError err: NSError?) { } } |
As you can probably guess the functions above are delegate methods that are called when the underlying MQTT client connects, publishes a message, subscribes to a topic, etc. It is up to you, the client writer, to fill out the implementation to suit your needs. In our case we’re going to implement the mqttDidDisconnect method as follows:
|
1 2 3 |
func mqttDidDisconnect(mqtt: MQTT, withError err: NSError?) { NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter().postNotificationName("DisconnectedNotification",object:nil) } |
I’ve mentioned in previous posts that I appreciate the flexibility of posting a notification and having it acted upon by whoever was listening for it. DisconnectedNotification will be handled in our main.swift routine.
main.swift
Let’s turn our attention to main.swift which will instantiate an MQTT-based client. At a fundamental level here is all that’s required:
|
1 2 3 4 |
let client = Client(clientId:"a-client-id") client.host = "broker.hivemq.com" client.connect() client.publish(topic:"/my/topic", withString:"my string") |
We want our client to be a bit more robust, so we’ll add in the ability to automatically reconnect if our connection is dropped by doing something like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
_ = NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter().addObserverForName("DisconnectedNotification", object:nil, queue:nil){_ in guard client.connect() else { print("Unable to connect to broker") exit(-1) } } |
Now, one could argue that we don’t want to exit if the connection to the broker fails. What we could do is set a timer and then rebroadcast our DisconnectedNotification. This will be our approach in the working code detailed further below.
We should publish something useful to the broker, so let’s set up an NSTimer to wake up every ten seconds and obtain the CPU temperature and then post that.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
let reportInterval = 10 let reportTemperature = NSTimer.scheduledTimer(NSTimeInterval(reportInterval), repeats:true){_ in if let cpuTemperature = CPU().temperature { _ = client.publish(topic:"/(client.clientId)/cpu/temperature/value", withString:String(cpuTemperature)) } } reportTemperature.fire() NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().addTimer(reportTemperature, forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode) NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().run() |
It should be noted here that we set the timer up and then fire() it immediately (so we’re not waiting ten seconds for that first post). Also, you will notice that we’re posting to the topic /<i>clientid</i>/cpu/temperature/value. This is one example of an MQTT topic naming convention and meant strictly as such. As you delve further into designing IoT applications it will become apparent that your naming convention is of considerable importance.
Getting the CPU Temperature
I love working with Linux and the wealth of information that is available in the /sys and /proc filesystems. Unfortunately when you’re dealing with hardware you have to frequently tailor your code to the specific hardware it’s running on. For example, on my x86 server the temperature of the CPU can be obtained by reading /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/temp1_input. On the BeagleBoard X15 it is at /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon1/temp1_input. That’s aggravating.
We won’t bother with writing portable code for now, but you should be able to take this example and suit it to your own system’s needs:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
struct CPU { var temperature:Double? { get { let BUFSIZE = 16 let pp = popen("cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/temp1_input", "r") var buf = [CChar](repeating:0, count:BUFSIZE) guard fgets(&buf, Int32(BUFSIZE), pp) != nil else { pclose(pp) return nil } pclose(pp) let s = String(String(cString:buf).characters.dropLast()) if let t = Double(s) { return t/1000 } else { return nil } } } } |
Putting it All Together
Let’s put everything together to build a working MQTT client that posts our CPU temperature to broker.hivemq.com. As a bonus, we’ll provide a web page that shows the CPU temperature displayed as a gauge.
We have three files that make up our client:
Client.swiftCPU.swiftmain.swift
Each of these files should go in the Sources directory. Let’s look at a complete implementation of each:
Client
Client.swift
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 |
import swiftlog import Foundation import MQTT class Client:MQTT, MQTTDelegate { init(clientId:String) { super.init(clientId:clientId) super.delegate = self } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didConnect host: String, port: Int) { SLogInfo("MQTT client has connected to \(host):\(port)") NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter().postNotificationName("ConnectedNotification", object:nil) } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didConnectAck ack: MQTTConnAck) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didPublishMessage message: MQTTMessage, id: UInt16) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didPublishAck id: UInt16) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didReceiveMessage message: MQTTMessage, id: UInt16 ) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didSubscribeTopic topic: String) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqtt(mqtt: MQTT, didUnsubscribeTopic topic: String) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqttDidPing(mqtt: MQTT) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqttDidReceivePong(mqtt: MQTT) { ENTRY_LOG() } func mqttDidDisconnect(mqtt: MQTT, withError err: NSError?) { SLogInfo("Disconnected from broker") NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter().postNotificationName("DisconnectedNotification",object:nil) } } |
CPU
CPU.swift
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import Glibc struct CPU { var temperature:Double? { get { let BUFSIZE = 16 let pp = popen("cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/temp1_input", "r") var buf = [CChar](repeating:0, count:BUFSIZE) guard fgets(&buf, Int32(BUFSIZE), pp) != nil else { pclose(pp) return nil } pclose(pp) let s = String(String(cString:buf).characters.dropLast()) if let t = Double(s) { return t/1000 } else { return nil } } } } |
main
Our main.swift appears to be complicated but it’s not really. The key things to recognize is that we wait for notifications and then set timers based upon those notifications to put our client into motion. For example, nothing good will come of trying to publish if we don’t have an MQTT connection established, so we wait for that notification (from our delegate) before attempting. Once a connection is established we set a 10 second timer and then update the temperature if we are still connected.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
import swiftlog import Glibc import Foundation slogLevel = .Info // Change to .Verbose to get real chatty slogToFile(atPath:"/tmp/pubSysTemp.log") let BUFSIZE = 128 var buffer = [CChar](repeating:0, count:BUFSIZE) guard gethostname(&buffer, BUFSIZE) == 0 else { SLogError("Unable to obtain hostname") exit(-1) } let client = Client(clientId:String(cString:buffer)) client.host = "broker.hivemq.com" client.keepAlive = 10 let nc = NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter() var reportTemperature:NSTimer? _ = nc.addObserverForName("DisconnectedNotification", object:nil, queue:nil){_ in SLogInfo("Connecting to broker") reportTemperature?.invalidate() if !client.connect() { SLogError("Unable to connect to broker.hivemq.com, retrying in 30 seconds") let retryInterval = 30 let retryTimer = NSTimer.scheduledTimer(NSTimeInterval(retryInterval), repeats:false){ _ in nc.postNotificationName("DisconnectedNotification", object:nil) } NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().addTimer(retryTimer, forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode) } } _ = nc.addObserverForName("ConnectedNotification", object:nil, queue:nil) {_ in let reportInterval = 10 reportTemperature = NSTimer.scheduledTimer(NSTimeInterval(reportInterval), repeats:true){_ in if client.connState == .CONNECTED { if let cpuTemperature = CPU().temperature { _ = client.publish(topic:"/\(client.clientId)/cpu/temperature/value", withString:String(cpuTemperature)) SLogInfo("Published temperature to \(cpuTemperature)") } else { SLogError("Unable to obtain CPU temperature") } } else { SLogError("MQTT client is not connected") } } NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().addTimer(reportTemperature!, forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode) } nc.postNotificationName("DisconnectedNotification", object:nil) // Kick the connection let heartbeat = NSTimer.scheduledTimer(NSTimeInterval(30), repeats:true){_ in return} NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().addTimer(heartbeat, forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode) NSRunLoop.currentRunLoop().run() |
Note also the use of a heartbeat timer. Runloops will exit if there are no input sources or timers attached to it, so we use a simple repeating timer to keep a heartbeat (and thus, the runloop) going.
Your Package.swift file should look like:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
import PackageDescription let package = Package( name: "PubSysTemp", dependencies:[ .Package(url:"https://github.com/iachievedit/MQTT", majorVersion:0, minor:1) ] ) |
To make life easier you can grab our code from GitHub. Build with swift build and then run it:
# git clone https://github.com/iachievedit/PubSysTemp # cd PubSysTemp # swift build # .build/debug/PubSysTemp
Remember: this code is written in Swift 3.0! For more information see our post on obtaining Swift 3.0 for Linux.
What’s this Broker Thing Again?
Think of an MQTT broker as an NSNotificationCenter. In iOS one typically obtains a reference to the NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter() and then posts messages to it. Likewise, to receive a message you register to be called when a named notification is posted (topic anyone?).
With MQTT you need to communicate with a broker. If you’re building an IoT gateway you might run your own broker using Mosquitto or HiveMQ. If you’re writing a tutorial on MQTT you might take advantage of a public broker such as test.mosquitto.org or broker.hivemq.com rather than running your own (like we did!).
In our example above we wrote an MQTT client that publishes data. What about subscribing to that data? This is also the purview of MQTT clients. For our example we’ll use a nice temperature gauge widget to power our temperature display.
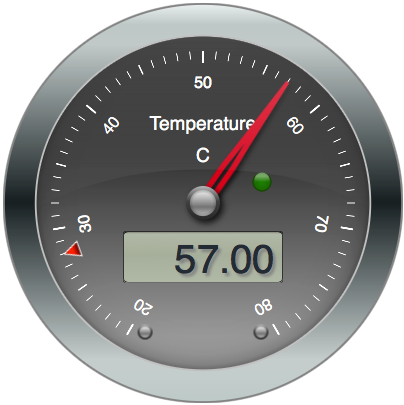
What’s important to realize here is that the temperature gauge is actually an (JavaScript-based) MQTT client that has subscribed to receive events published to the /darthvader/cpu/temperature/value topic on broker.hivemq.com. (darthvader is our client’s hostname.)
What’s Next
There’s much more to be done with the MQTT library. As of June 11, 2016 it successfully connects and publishes, but subscribing to a topic is another story. That’s our next issue to tackle.
This is just the beginning, however, for Swift on the server. Organizations such as Zewo are working hard to develop libraries that can be used to develop server-side software on Linux with Swift. In fact, our MQTT library uses Zewo’s VeniceX TCP routines for network IO. Time will tell, but I’m convinced Swift has a bright future ahead of it in more than just iOS development.
Postscript: Please don’t comment on my lousy voltage divider. I nearly failed EE classes and do the best I can.

Very interesting work Joe. I am a longtime fan of pub/sub, and it seems like a good fit for IoT.